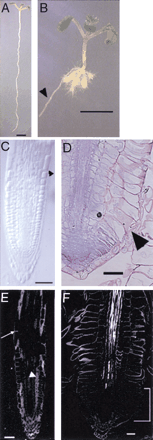
Phenotypic analysis of cobra.
(A) Wild-type and (B) cob-1 seedlings oriented vertically grown for 10 d on nutrient agar medium containing 4.5% sucrose. The conditional nature of cob can be seen in the lateral root, which has grown into the agar, thereby slowing its growth (arrowhead). (C) Cleared whole mount of wild-type root viewed with Nomarski optics. Arrowhead indicates the region where rapid longitudinal expansion begins. (D) Longitudinal section of cob root stained with toluidine blue. Abnormal lateral expansion is most apparent in the epidermis (arrowhead). (E,F) Polarized-light micrographs. (E) In wild type, strong retardance is observed in cell walls throughout the root, both in cross-sectioned walls (arrow) and in longitudinal faces of cells in the plane of section (arrowhead). (F) In cob-1, there is little retardance detected in the growing region of the root, in either the crosswalls or the longitudinal faces (bracket), indicating a reduction in crystalline cellulose microfibrils in this region. Bars in A and B = 0.25 cm. Bars in C-F = 50µm.